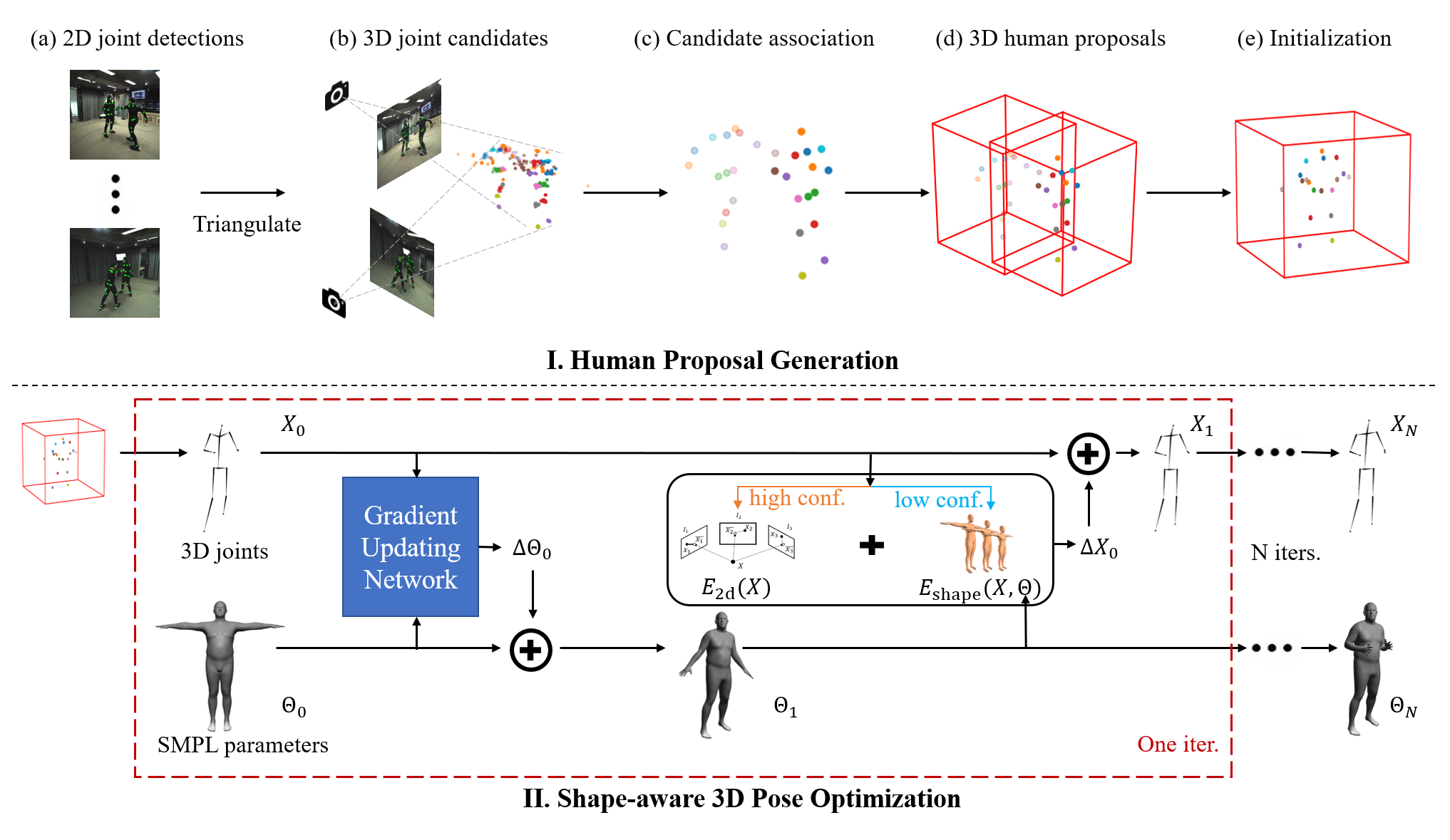
Pipeline structure. Stage I: (a): We apply a 2D human pose estimation method to obtain 2D joint candidates. (b): 2D candidate pairs with the same part label are triangulated into 3D space to produce 3D joint candidates. (c): A confidence-aware voting based algorithm is used for clustering joint candidates from partial observations. (d): The position of human instances can be detected based on a reliable joint. (e): For each 3D human proposal, we project it back into the image space and leverage the part affinity field feature (PAF) to filter the joint candidates from closely interacting people and obtain initial 3D pose proposals. Stage II: We refine the initial 3D poses X0 by optimizing a 2D-3D objective. Both 3D poses X and SMPL parameters Θ are optimized alternatively. For each iteration, the 3D joint locations X are optimized by a 2D re-projection error when the corresponding 2D joint detections are of high confidence. To obtain kinematically plausible poses, we leverage updated SMPL estimation for regularizing the low-confidence 3D joint candidates. The SMPL parameters Θ are encouraged to align to the updated 3D poses in each iteration via a learned gradient updating network. After a small number of iteration, our method can generate complete and accurate 3D human poses and output SMPL parameters.
Abstract
In this paper we contribute a simple yet effective approach for estimating 3D poses of multiple people from multi-view images. Our proposed coarse-to-fine pipeline first aggregates noisy 2D observations from multiple camera views into 3D space and then associates them into individual instances based on a confidence-aware majority voting technique. The final pose estimates are attained from a novel optimization scheme which links high-confidence multi-view 2D observations and 3D joint candidates. Moreover, a statistical parametric body model such as SMPL is leveraged as a regularizing prior for these 3D joint candidates. Specifically, both 3D poses and SMPL parameters are optimized jointly in an alternating fashion. Here the parametric models help in correcting implausible 3D pose estimates and filling in missing joint detections while updated 3D poses in turn guide obtaining better SMPL estimations. By linking 2D and 3D observations, our methodis both accurate and generalizes to different data sources because it better decouples the final 3D pose from the inter-person constellation and is more robust to noisy 2D detections. We systematically evaluate our method on public datasets and achieve state-of-the-art performance.
